Overview
Satellite estimates of rainfall, like radar, are indirect. Satellite rainfall estimates are lower-resolution than radar estimates but are more consistent from one location to another.
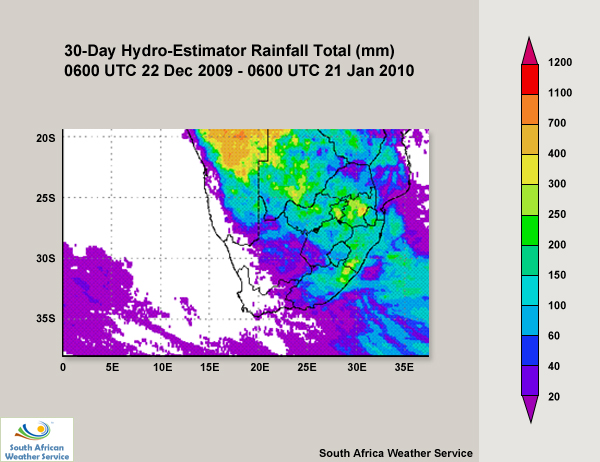
A common satellite tool, the hydro-estimator (HE), indicates how much rainfall (in mm) has accumulated over a given region during a specified period and is useful for determining whether to issue warnings for heavy rainfall and flash flooding. HE precipitation estimates are based on cloud-top temperatures derived from satellite imagery. This makes them a good complement to radar data. But the HE is particularly valuable in data-sparse areas with limited ground-based observing systems, such as the Southern African Development Community (SADC - see map).
The South African Weather Service has an in-house version of the hydro-estimator, which uses the local version of the UK Met Office Unified Model and MSG satellite data. The product can be visualised with the SUMO software and internally at the SWFDP website hosted by SAWS. (Note that it's for use by member countries only.)